Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder that affects between 5-10% of us during our reproductive years. It's characterized by a hormonal imbalance that can impact our overall health and lead to a variety of symptoms, including significant changes in our menstrual cycles. Grasping what PCOS means for us is key to managing and treating it effectively.
Recognizing the
Symptoms of PCOS
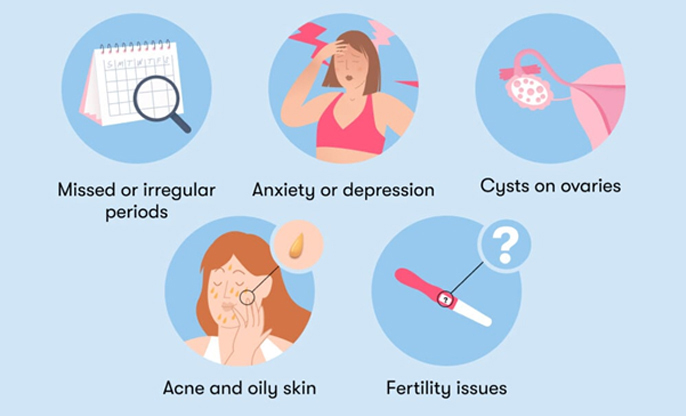
Symptoms of PCOS can vary widely among us, but here are
some common ones you might encounter:
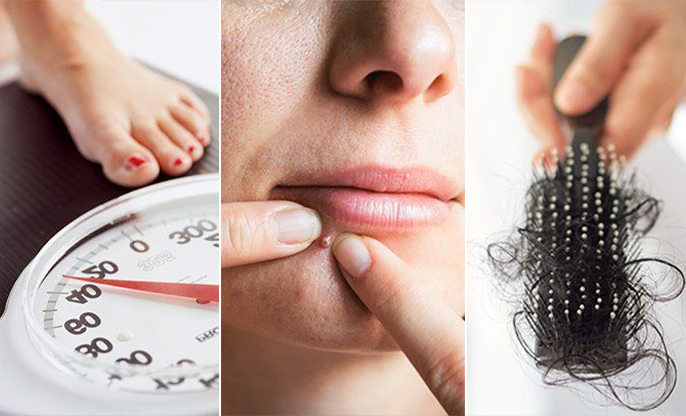
● Menstrual Irregularities: You
might find your periods are infrequent, irregular, or prolonged. Some of us may
have fewer than nine periods a year, or sometimes none at all.
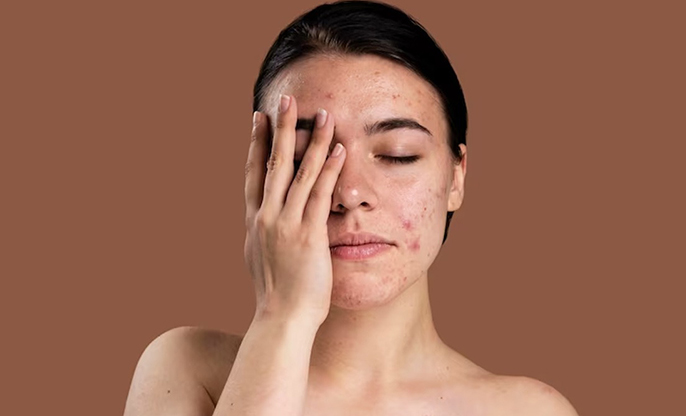
● Hyperandrogenism: Higher
levels of male hormones may lead to signs like excessive hair growth on the
face and body, severe acne, and even male-pattern baldness.
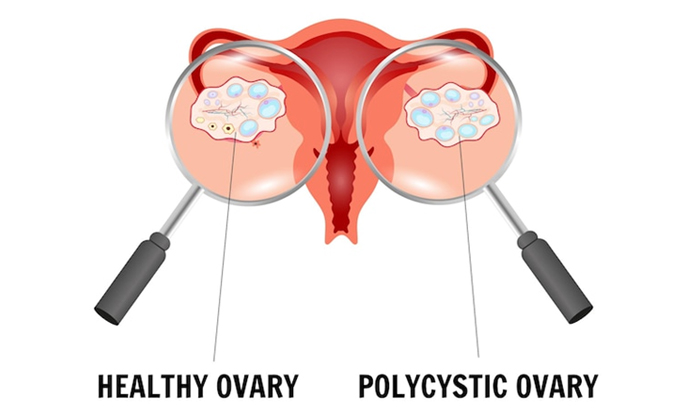
● Polycystic Ovaries: Although
not present in everyone, many of us might have enlarged ovaries that contain
numerous small cysts, detectable by ultrasound.
● Weight Gain: It’s also common to struggle with weight, particularly around the abdomen, which can make PCOS symptoms worse.
Exploring the
Causes of PCOS
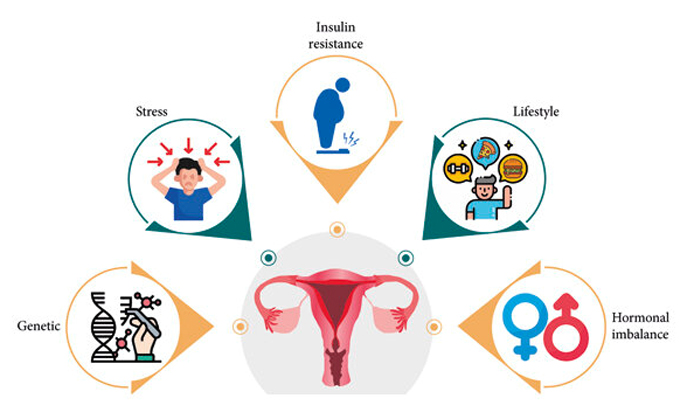
While the exact cause of PCOS isn't clear, several factors
seem to influence its development:
● Genetic Links: If PCOS runs in
your family, you might be more likely to develop it too.
● Insulin Resistance: Many of
us with PCOS have bodies that use insulin inefficiently, leading to higher
insulin levels that can increase androgen production and affect ovulation.
● Inflammation: Higher inflammation levels are also common and can contribute to higher androgen levels.
Managing PCOS
Though there’s no cure for PCOS, managing symptoms is
possible through lifestyle adjustments and medication:
● Lifestyle Changes: Staying
active and eating a balanced diet helps manage weight, improve how your body
uses insulin, and reduce symptoms.
● Medications: Options like
birth control pills can regulate your periods, reduce androgen levels, and help
with acne. For those trying to conceive, medications to induce ovulation can be
helpful. Metformin might also be prescribed to improve insulin resistance.
● Other Treatments: Treatments for hair removal and acne can help manage the more visible aspects of PCOS. In severe cases, anti-androgen medications may be considered.
PCOS and Your
Periods
Irregular periods are a defining symptom of PCOS. The hormonal imbalance often prevents the ovaries from developing and releasing eggs regularly, which can lead to irregular or missed periods and even infertility due to the lack of consistent ovulation.
Long-Term Health
Considerations
Without management, PCOS can lead to serious health issues
like type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, hypertension, heart disease, and an
increased risk of endometrial cancer. An early diagnosis and proactive
management can greatly reduce these risks.
Understanding PCOS is crucial for managing your health. With the right lifestyle choices and medical care, many of us can effectively manage our symptoms and reduce the impact of PCOS on our lives. If you think you might have PCOS, a conversation with your doctor can be the first step toward feeling better.