Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a part of many of our lives, affecting everything from our menstrual cycles to our appearance and fertility. Understanding our bodies and managing symptoms effectively is essential for us.
What is PCOS?
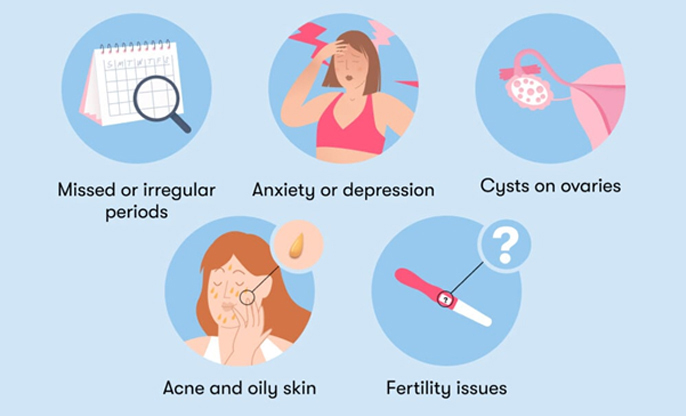
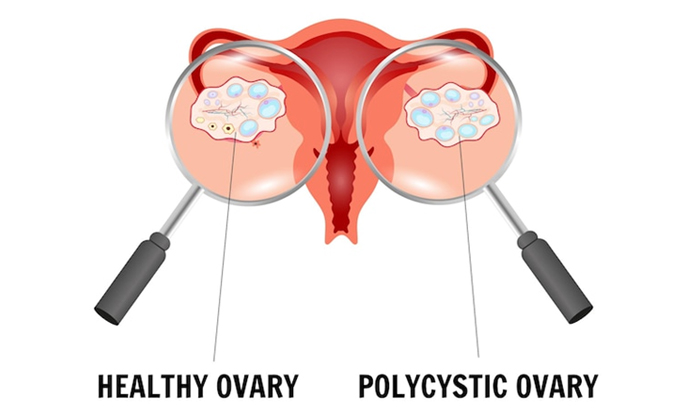
PCOS is a hormonal disorder with several manifestations:
● Cysts on the Ovaries: Our
ovaries might be enlarged and contain fluid-filled sacs.
● Irregular Menstrual Cycles: We might
experience unpredictable or infrequent menstrual periods.
● High Levels of Androgens: This can lead to unwanted hair growth, severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
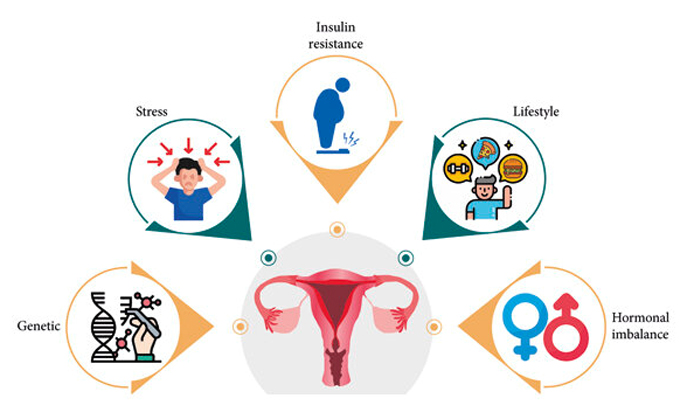
Why Does PCOS
Occur?
While the exact cause of PCOS isn't fully understood,
several factors contribute:
● Genetics: A family history
of PCOS increases our likelihood of developing it.
● Insulin Resistance:
Difficulty using insulin properly can raise androgen levels, disrupting
ovulation.
● Inflammation: Higher levels of body inflammation may affect hormone levels.
Symptoms to Be
Aware Of
● Varying
menstrual patterns or absent periods.
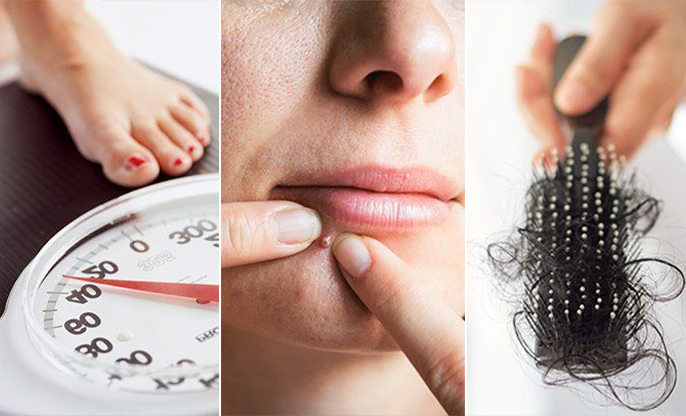
● Unwanted
facial and body hair, acne, and thinning scalp hair.
● Challenges
with fertility due to irregular ovulation.
● Weight
gain, particularly around the abdomen.
● Dark patches of skin and skin tags in various body folds.
Diagnosis Process
● Discussion with Our Doctor: Talking
about our symptoms and medical history.
● Physical Examination: Our
doctor might check for physical signs like hair growth and acne.
● Blood Tests: These help check
hormone levels and rule out other issues.
● Ultrasound: This examines our ovaries for cysts and checks the uterine lining.
How to Manage
PCOS?
● Lifestyle Adjustments: A
balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage our weight and reduce blood
sugar levels.
● Medication Options: Birth
control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles and manage symptoms like hair
growth and acne. Metformin may be used for insulin resistance.
● Fertility Treatments: For those trying to conceive, medications can help stimulate ovulation.
Living with PCOS is about understanding our condition and making informed choices about our health. With the right strategies, we can manage our symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. It's about learning, adapting, and supporting each other through our journeys.