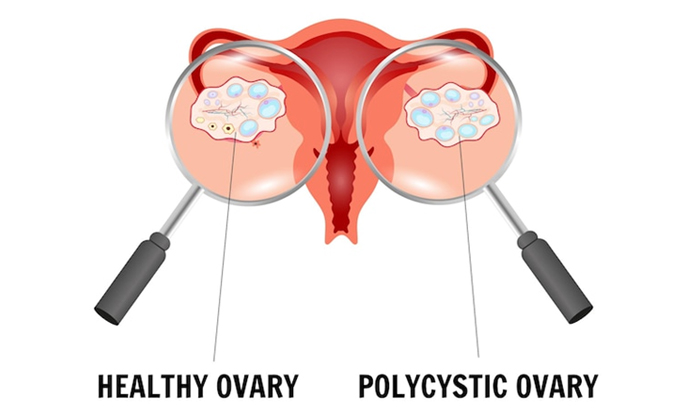
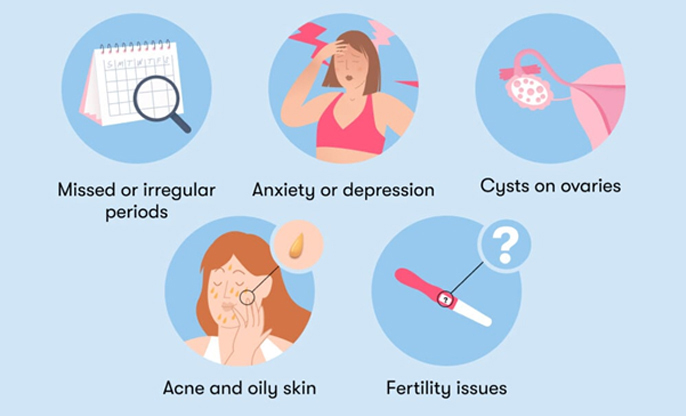
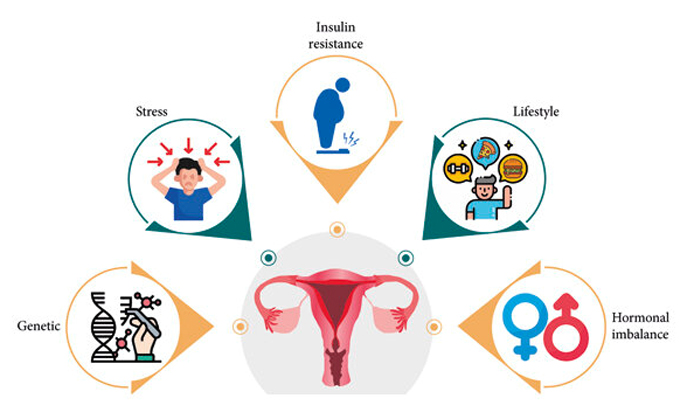
Living with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is also about taking back control of our bodies and our health. Here’s how we use medications to help manage the diverse symptoms of PCOS:
- Hormonal Contraceptives
○ Why We Use Them: To help regulate
our menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels that cause unwanted hair growth and
acne.
○ How They Help: These pills work
by reducing androgen production by our ovaries, helping to stabilize our
hormones and promote regular menstrual cycles.
○ Common Options: We might use combination oral contraceptives like Yaz, Ortho Tri-Cyclen, or Estrostep.
- Anti-Androgens
○ Our Purpose: To fight against
the effects of excess male hormones that contribute to acne and hirsutism.
○ Action: These
medications block androgens from affecting our skin and hair follicles.
○ Typical Choice: Spironolactone (Aldactone) is a go-to for many of us battling these symptoms.
- Metformin
○ Why It’s Part of Our Routine: It’s
essential for those of us struggling with insulin resistance, a frequent
challenge in PCOS.
○ Benefits: Metformin helps our bodies use insulin more effectively, which can lower blood sugar levels, decrease androgen levels, and improve our menstrual cycles and weight management.
- Clomiphene Citrate
○ Why We Take It: For many of us
wanting to conceive, this medication helps stimulate ovulation.
○ How It Works: It encourages
our pituitary gland to release the hormones necessary for ovulation.
○ Commonly Known As: Many of us know it as Clomid.
- Gonadotropins
○ Our Last Resort: When other
treatments haven’t worked, these fertility medications are a next step.
○ What They Do: These hormones are injected to directly stimulate our ovaries to produce eggs, crucial for those of us who have not responded to simpler treatments.
- Letrozole
○ A Newer Approach: It’s
gaining traction as an effective way to induce ovulation.
○ The Science: By reducing
estrogen levels, it prompts our pituitary gland to produce more
follicle-stimulating hormone, which can lead to the development of mature eggs.
○ Why It’s Promising: Studies are showing it might be more effective than Clomid for some of us looking to get pregnant.
While there’s no outright cure for PCOS, these medications offer us a way to manage our symptoms effectively and improve our quality of life. Each of us may need a different combination, tailored to our specific symptoms and health goals. Alongside these medications, embracing healthy lifestyle changes like a balanced diet and regular exercise remains critical. Together, we take these steps, not just to manage PCOS, but to thrive despite it.