Understanding the Dermatological Impact
PCOS deeply affects our skin and hair too, areas that profoundly influence how we feel about ourselves. Let's delve into how PCOS impacts our dermatological health and explore ways to care for our skin and hair while managing this complex condition.
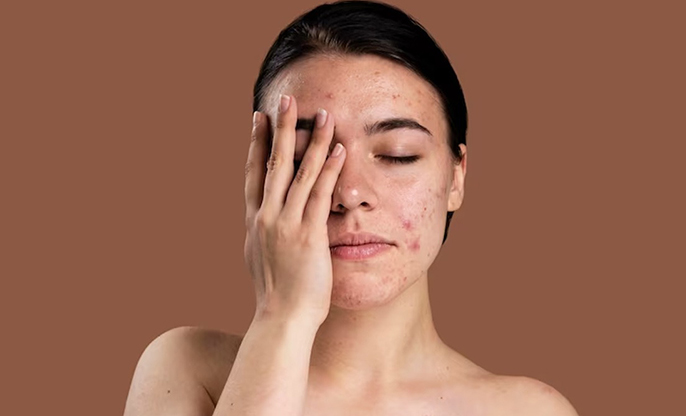
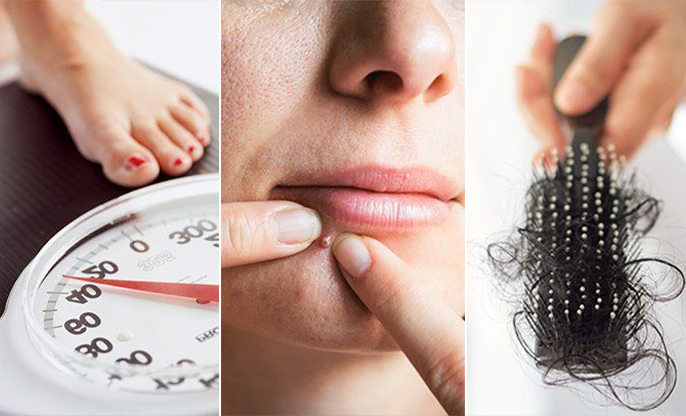
PCOS and Our Skin
● Acne: I often battle
with stubborn, severe acne that clings to the lower face, jawline, and neck.
This isn't just typical acne; it’s driven by the excess androgens in our
bodies, which rev up the oil glands in our skin.
● Hirsutism: Excessive hair
growth, or hirsutism, shows up in areas like the face, chest, and back - places
where it can be especially distressing. This too is linked to those high
androgen levels.
● Acanthosis Nigricans:
Darkened patches of velvety skin in the creases of our necks, armpits, and
groin point to insulin resistance, a frequent companion of PCOS.
● Seborrheic Dermatitis: This skin condition brings scaly patches and redness, mostly on our scalp, adding to our frustrations.
PCOS and Our Hair
● Thinning Hair: The very androgens
causing hair where we don’t want it can thin out what’s on our scalp. This
androgenic alopecia is more noticeable at the scalp's top and becomes even more
of a challenge post-menopause.
● Brittle Hair: Our hair not only falls but becomes dry and brittle, another testament to the hormonal turmoil inside.
Caring for Our
Skin and Hair
● Skincare Treatments:
○ Topical
agents like retinoids can fight acne effectively.
○ Professional
interventions like chemical peels or laser therapy address severe skin
symptoms.
● Hair Care Strategies:
○ Minoxidil,
applied topically, encourages hair regrowth.
○ A
nutritious diet and regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity,
which may indirectly help stabilize our hair’s life cycle.
● Combating Insulin Resistance:
○ Embracing
a low-glycemic diet aids in managing glucose levels and improves insulin
response, crucial for us.
○ Medications
like Metformin also enhance insulin sensitivity, helping to alleviate both skin
and hair troubles.
● Hormonal Treatments:
○ Birth
control pills regularize periods and lower androgen levels, easing many of our
skin and hair woes.
○ Anti-androgens such as spironolactone can cut down on unwanted hair growth and clear up acne.
PCOS touches every part of our lives, but by understanding how it affects our skin and hair, we can target treatments more effectively and reclaim our confidence. Each step in treatment and lifestyle adjustment is a step towards feeling more like ourselves, moving past the visible signs of PCOS and embracing holistic well-being.