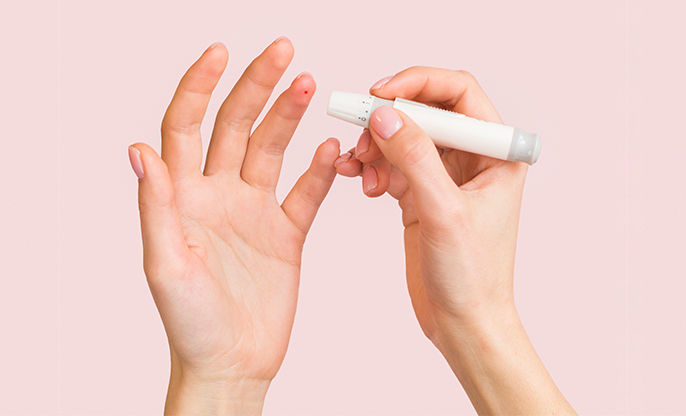
The glucose tolerance test, also known as the oral glucose tolerance test, measures your body's response to sugar (glucose). This test can be used to screen for type 2 diabetes but more commonly, a modified version of this test is used to diagnose gestational diabetes — a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy.
TWO-STEP TESTING
During the first step, you will have a glucose screening test:
- You do not need to prepare or
change your diet in any way.
- You will be asked to drink a
liquid that contains glucose.
- Your blood will be drawn 1 hour after you drink the glucose solution to check your blood glucose level.
If your blood glucose from the first step is too high, you will need to come back for a 3-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- You shouldn’t eat or drink (other
than sips of water) for 8 to 14 hours before your test.
- You will be asked to drink a
liquid that contains glucose, 100 grams.
- You will have blood drawn before
you drink the liquid, and again 3 more times every 60 minutes after you drink
it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 3 hours for this test.
ONE-STEP TESTING
You need to go to the lab one time for a 2-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- You shouldn’t eat or drink (other
than sips of water) for 8 to 14 hours before your test.
- You will be asked to drink a
liquid that contains glucose, 75 grams.
- You will have blood drawn before
you drink the liquid, and again 2 more times every 60 minutes after you drink
it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 2 hours for this
test.
Results
TWO-STEP TESTING
Most of the time, a normal result for the
glucose screening test is a blood sugar that is equal to or less than 140 mg/dL
(7.8 mmol/L) 1 hour after drinking the glucose solution. A normal result means
you do not have gestational diabetes.
If your blood glucose is higher than 140
mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L), the next step is the oral glucose tolerance test. This test
will show if you have gestational diabetes. However, most women (about 2 out of
3) who take this test do not have gestational diabetes.
ONE-STEP TESTING
If your blood glucose level is lower, you do
not have gestational diabetes.
If only one of your blood glucose results in the glucose tolerance test is higher than normal, your care-provider may simply suggest you to change some of the foods you eat. Then, your care-provider may test you again after you have changed your diet. If more than one of your blood glucose results is higher than normal, you have gestational diabetes.