Clinical and evident symptoms of physiological anemia
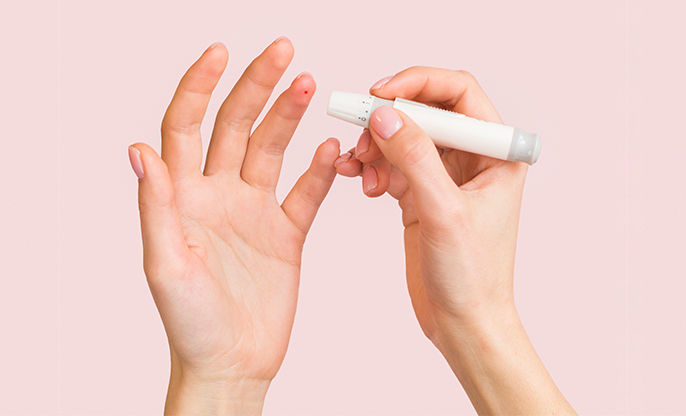
Suppose a complete blood count (CBC)
of a pregnant woman reveals that the red blood cells in the body, which
transport oxygen throughout the body to its different parts, tissues, and
muscles, are low. What does it mean? It indicates a lack of adequate iron
content in the body. In this case, you may suffer from a medical condition
called physiological anemia.
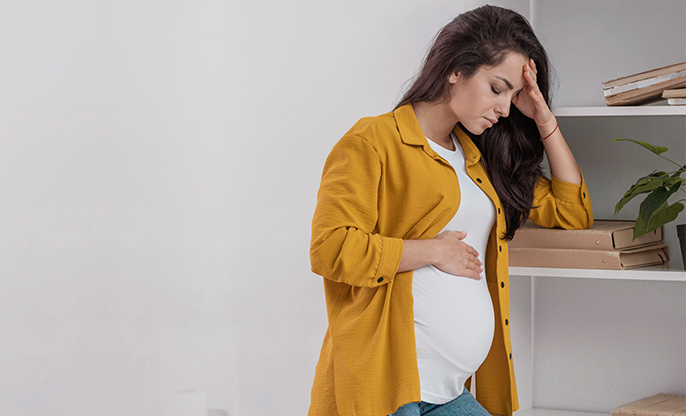
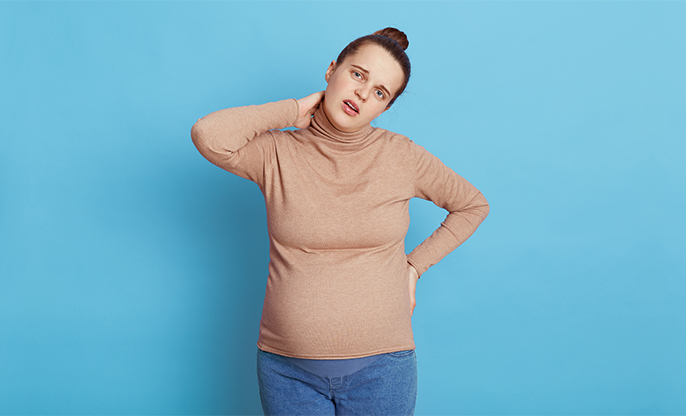
Low iron stores may make you weary,
dizzy, tired, drowsy, sluggish, chilly, and out of breath. Diet changes can
usually help you avoid anemia during pregnancy, but other measures must be
taken if the iron levels continue to deplete. Anemia is the sole cause of
almost 20-40% of maternal deaths and must be considered seriously.
Feeling weak and exhausted when
pregnant is a symptom of physiological anemia. Understand the symptoms, risk factors,
and what can be done to prevent this condition. Because of the increasing fetal
demands, you are more likely to develop anemia if you are pregnant. When you
have iron deficiency anemia, your red blood cells aren't healthy enough to
carry enough oxygen to the body's tissues.
What signs of anemia do you
experience while pregnant?
Mild anemia may not make any of its
symptoms obvious initially. But, if the stores or iron keep depleting, you
might experience the following:
Light-headedness and dizziness
Headaches
Tachycardia
Exhaustion
Cold
Respiration difficulty
Weakness and lethargy
Rapid heart rate
Headache
Fragile, dry, pale, and bruised
skin
Tingling aching tongue
Syncope
Reduced exercise tolerance
Restless legs syndrome or unintended
flexion of the lower leg
Your baby can not reach a healthy
weight if you have anemia and maybe born prematurely with low birth weight. A
basic blood test advised by the doctor to check the levels of Haemoglobin or
hematocrit reveals physiological anemia, and its severity will affect the
course of treatment. To prevent anemia during pregnancy, you need a healthy
diet.
The doctor might ask if you show
signs of an extreme craving or desire to eat ice, sand, or chalk. He will check
out for blue sclera and pale dull conjuctiva. Furthermore, cold feet, hands and
skin of pale yellow color, brittle, grooved nails, vertigo, spinning, inflamed
tongue, breathlessness, chest pain, fall in appetite, etc., also indicate a
fall in iron levels.
Further checks include difficulty
focusing, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, frequent sore throats, leg
edema, stomatitis, glossitis, pica, and functional heart murmur. The healthcare
worker keenly observes the symptoms mentioned above and signs because mild
signs are often mistaken as pregnancy symptoms.
Signs intensify as iron deficiency
increases. So, do not try to self-treat or self-diagnose your condition.
Professional help is critical. Iron supplements and other prenatal medications
need to be taken under supervision. Excess iron accumulation can also be
dangerous, leading to bodily and liver complications.
Mild anemia can be treated with
supplements and prenatal vitamins to maintain the folic acid, iron, and Vitamin
B 12 levels. Severe anemia is indicated if the hemoglobin levels of the
pregnant woman are around 6 – 8 grams per decilitre, and there is no other
option but an infusion.
Only low red blood cell counts indicate physiological anemia because other evident symptoms can be clouded or mistaken. The prenatal examination and a blood test can reveal the amount of Haemoglobin and hematocrit to check oxygen levels and RBC in the blood. For the safety of the mother and fetus, the body must have healthy red blood cell levels during the pregnancy.