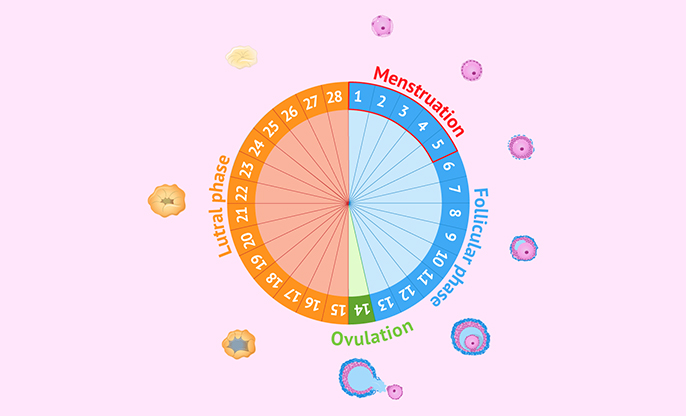
Menstruation is a natural part of your health and fertility journey, yet every woman experiences it differently. Getting to know what a 'normal' menstrual cycle looks like for you can help you manage your reproductive health more effectively and pinpoint any potential concerns.
The Range of
Normal Menstrual Cycles
● Duration: Most cycles run
between 21 and 35 days, but anywhere within this range is considered normal.
The bleeding itself usually lasts from 2 to 7 days. If you find that you
typically bleed for around 4 to 5 days, that’s quite common.
● Frequency and Regularity: A
'regular' cycle is one that consistently occurs at similar intervals—be it
every 24, 28, 32, or 35 days. This regularity shows that your body is working
predictably. Yet, it's also perfectly normal if your cycle varies by a few days
here and there.
● Volume of Menstrual Flow: How much you bleed can vary too. Most women lose about 30 to 80 milliliters of blood per cycle, with the average being around 40 milliliters. You might use about 3 to 6 pads or tampons a day, which helps you figure out if your flow is light, moderate, or heavy.
When Your
Menstruation Might Seem Irregular
Sometimes your cycle might feel like it’s off track - maybe the length changes significantly from one month to the next, or perhaps you skip periods without being pregnant. These irregularities might signal something like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid issues, or hormonal imbalances, and it’s worth paying attention to these signs.
Factors That
Influence Your Menstrual Cycle
● Age: It’s common for
your periods to be a bit irregular when they first begin and as you approach
menopause.
● Lifestyle: Your stress
levels, diet, and how much you exercise can all influence your cycle and
hormonal balance.
● Health Conditions: Certain
conditions and medications can impact the regularity and nature of your
menstrual cycle.
● Reproductive Health Issues: Problems
like PCOS, endometriosis, or fibroids can cause your periods to be irregular or
painful.
When to Reach Out
for Help?
If you notice significant changes in your cycle’s length,
frequency, or flow, or if you experience severe pain that disrupts your daily
life, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor. Also, if there are gaps of 90 days
or more without menstruation (and you’re not pregnant), or if you have bleeding
between periods or after sex, seeking medical advice is important.
Understanding what’s normal for your body can empower you to take charge of your health. Keeping track of your menstrual patterns can be incredibly helpful, not just for you but also for your healthcare provider in diagnosing and managing any potential issues effectively.