When Prolactin Levels Rise
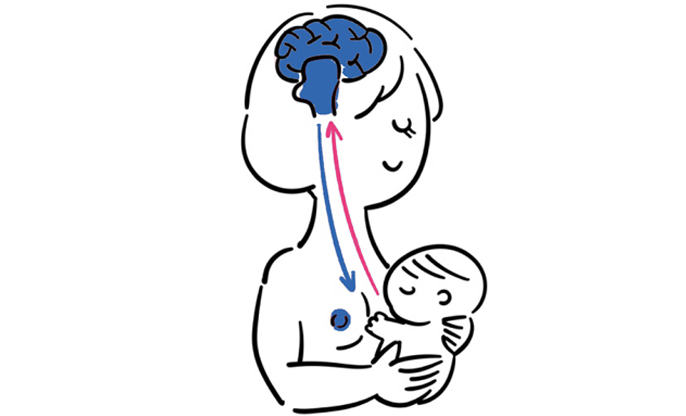
Living with hyperprolactinemia means I’m dealing with more prolactin in my blood than usual. Prolactin is that hormone from the pituitary gland, mostly known for its role in breastfeeding, but it’s also got a big say in my menstrual cycle and fertility.
What Exactly Is
Going On?
Hyperprolactinemia happens when my pituitary gland goes a bit overboard, pumping out more prolactin than my body actually needs. It's a fairly common hiccup with the pituitary, and more often than not, it picks on us women, messing with our reproductive systems.
Why Do I Have
High Prolactin Levels?
Well, it could be a few things:
● Pituitary Disorders: Like
prolactinomas, those small benign tumors that form right on the pituitary
gland.
● Medications: Some of the meds
for mood disorders, or even the ones for high blood pressure, can hike up
prolactin levels.
● Thyroid Troubles: If my
thyroid is lagging (hypothyroidism), that could be nudging my pituitary gland
to make more prolactin.
● Other Health Issues: Things
like kidney disease or PCOS might be culprits.
● Stress: Yes, just plain old stress from being sick or in pain can spike prolactin temporarily.
What I Feel
Depending on whether you’re a woman or a man, symptoms can
look different, but here’s what us women might face:
● Menstrual
hiccups like irregular periods or no periods at all.
● Unexpected
milk production, which is both surprising and confusing when you’re not
breastfeeding.
● Trouble
getting pregnant.
● Less interest in those intimate moments.
Getting to the
Bottom of It
To figure this out, I’d go through:
● Blood Tests: This checks how
much prolactin I actually have floating around.
● MRI: A good look at
my pituitary gland to see if there’s a tumor.
● Physical Checks: Looking for any signs of milk production when it’s not expected.
How to Handle It?
● Medication: Drugs called
dopamine agonists are usually the first choice to get those prolactin levels
down.
● Addressing Other Issues: If it’s
my thyroid acting up, treating that might sort out the prolactin too.
● Surgery: Sometimes, if
there’s a big tumor, or meds aren’t doing the trick, surgery might be the way
to go.
● Keeping Tabs: Regular checks to make sure everything’s staying on track with the treatment.
It’s a lot to take in, knowing something as small as a hormone can throw off so much. If any of these symptoms sound familiar, it’s crucial to talk to a healthcare provider. Catching this early means we can manage it before it leads to more serious stuff like bone problems or messing with my chances of having a baby.