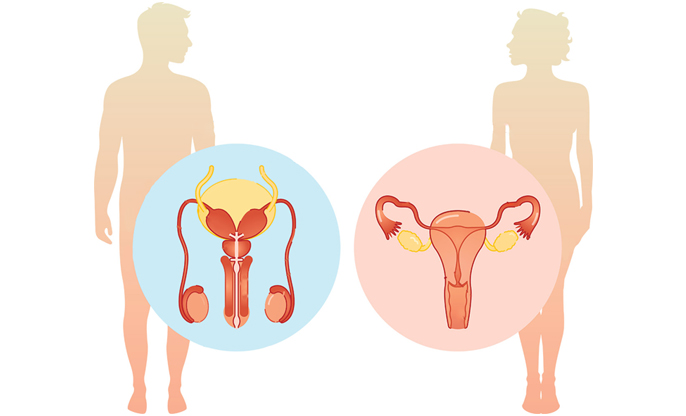
Our bodies are intricate and beautifully complex, especially when it comes to the reproductive systems of both males and females. These systems do more than just enable us to create life; they play vital roles in maintaining our overall health. Through this article, let’s find out how each system works, both individually and together, to support human reproduction and overall wellness.
Male Reproductive
System
The male reproductive system is tailored primarily for
producing and delivering sperm. Here’s how it’s structured:
● Testes: These are the
powerhouses that produce sperm and testosterone, shaping male secondary sexual
characteristics like muscle mass and body hair.
● Epididymis: After sperm are
produced, they’re sent here to mature and be stored until needed.
● Vas Deferens: This is the
pathway sperm follow during ejaculation, moving from the epididymis through to
the urethra.
● Urethra: This duct has a
dual role—it expels urine from the bladder and acts as a channel for sperm
during ejaculation.
● Seminal Vesicles and Prostate Gland: These
structures produce fluids that form part of semen, providing nourishment and a
means of transport for sperm.
● Penis: This organ plays a crucial role in sexual intercourse by delivering semen into the female reproductive tract.
Female
Reproductive System
Designed to produce eggs, receive sperm, support
fertilization, and nurture a developing baby, the female reproductive system
includes:
● Ovaries: These small
glands on either side of the uterus produce eggs and hormones like estrogen and
progesterone.
● Fallopian Tubes: These are the
pathways that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This is also where
fertilization typically occurs.
● Uterus: Also known as
the womb, this muscular organ is where a fertilized egg will implant and grow
throughout pregnancy.
● Cervix: This is the
lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina and dilates during
childbirth to allow the baby to pass through.
● Vagina: Serving as both the receptacle for the penis during sexual intercourse and the birth canal during childbirth, the vagina is a central player in the reproductive process.
How Male and
Female Systems Interact?
The magic happens when these systems come together:
● Sexual Intercourse:
Intercourse allows semen, carrying sperm, to be ejaculated into the female
reproductive tract.
● Fertilization: Sperm journey to
the fallopian tubes, where they may meet an egg. If one sperm successfully
fertilizes the egg, it becomes an embryo and begins its journey to the uterus.
● Pregnancy: Once the embryo implants in the uterus, a beautiful and complex process unfolds, supported by critical hormones produced by the ovaries and later, the placenta.
Beyond
Reproduction
Both systems also significantly impact individual health
through hormonal regulation and structural support:
● Hormonal Regulation: In men,
testosterone influences muscle strength, bone density, and red blood cell
production. In women, estrogen and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle,
support bone health, and can influence mood.
● Structural Support: Beyond their reproductive roles, organs like the prostate in males and the uterus in females contribute to hormonal balance and disease resistance.
Our reproductive systems are not just about making babies; they're key components of our overall health and well-being. By appreciating and caring for these systems, we embrace a fuller understanding of our bodies, empowering us to take better care of ourselves and each other.








